| Identification | More | [Name]
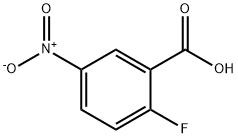
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid | [CAS]
7304-32-7 | [Synonyms]
2-FLUORO-5-NITROBENZOIC ACID
BUTTPARK 32\01-76
RARECHEM AL BO 0445
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid 98%
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoicacid98%
2-FLUORO-5-NITRROBENZOIC ACID
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzotc acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
627-772-7 | [Molecular Formula]
C7H4FNO4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00134238 | [Molecular Weight]
185.11 | [MOL File]
7304-32-7.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to light yellow crystal powder | [Melting point ]
142-144 °C (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
337.7±27.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.568±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature | [solubility ]
Soluble in chloroform, ethanol. | [form ]
Crystalline Powder | [pka]
2.54±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White to pale yellow | [BRN ]
1912835 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C7H4FNO4/c8-6-2-1-4(9(12)13)3-5(6)7(10)11/h1-3H,(H,10,11) | [InChIKey]
ICXSHFWYCHJILC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)C1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC=C1F | [CAS DataBase Reference]
7304-32-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [Hazard Note ]
Irritant | [HazardClass ]
IRRITANT | [HS Code ]
29163990 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white to light yellow crystal powder | [Uses]
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid may be used in the synthesis of:
- dibenz[b,f]oxazepin-11(10H)-ones, via the nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) of fluorine in 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid with the OH of various 2-aminophenols on solid support
- synthesis of substituted dibenzazocines on solid support, via SNAr of fluorine in 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid with the OH function of the immobilized polysubstituted phenols
- in the synthesis of oxazepines
| [Uses]
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid may be used in the synthesis of dibenz[b,f]oxazepin-11(10H)-ones, via the nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) of fluorine in 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid with the OH of various 2-aminophenols on solid support, synthesis of substituted dibenzazocines on solid support, via SNAr of fluorine in 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid with the OH function of the immobilized polysubstituted phenols, in the synthesis of oxazepines. | [General Description]
2-Fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid is reported to react with an aldehyde, isonitrile and a primary amine tethered to a Boc-protected internal amino or hydroxyl nucleophile, to afford the Ugi product. | [Synthesis]
General procedure for the synthesis of 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid from o-fluorobenzoic acid: Nitric acid (60% solution, 5.0 mL) was slowly added dropwise to pre-cooled concentrated sulfuric acid (5.0 mL), and the reaction temperature was controlled to not exceed 10 °C. Subsequently, o-fluorobenzoic acid (2.1 g, 15.0 mmol) was added in batches and the reaction temperature was maintained between 15 and 25 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction was quenched by addition of ice water and the precipitate was collected by filtration. The product was dried at room temperature to give the intermediate 2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid as a white powder. Yield: 93%; Melting point: 135-137 °C; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=7.32 (t, 1H, H3, 3JH3_H4=JH3-F=9.2 Hz), 8.43 (dt, 1H, H4, 3JH4_H3=9.2 Hz, 4JH4_F=4JH4_H6=3.5 Hz), 8.89 (dd, 1H, H6, 4JH6_F=5.8 Hz, 4JH6_H4=3.0 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ=118.7 (d, C1, 2JC-F=10.9 Hz), 118.7 (d, C3, 2JC-F=25.0 Hz), 128.9 (d, C6, 3JC -F=2.2 Hz), 130.6 (d, C4, 3JC-F=10.9 Hz), 143.9 (C5), 165.7 (d, C2, 1JC-F=272.0 Hz), 166.7 (d, COOH, 3JC-F=3.8 Hz). | [References]
[1] Patent: WO2012/85003, 2012, A1. Location in patent: Page/Page column 83
[2] Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2008, vol. 73, # 2, p. 538 - 549
[3] Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1998, vol. 35, # 6, p. 1301 - 1304
[4] Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003, vol. 46, # 10, p. 1905 - 1917
[5] Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1981, vol. 34, # 5, p. 969 - 979 |
|
|