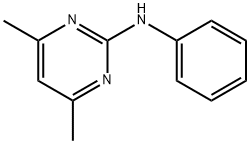
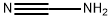| Identification | More | [Name]
Pyrimethanil | [CAS]
53112-28-0 | [Synonyms]
2-AMINOPHENYL-4,6-DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINE
2-ANILINO-4,6-DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINE
4,6-DIMETHYL-N-PHENYL-2-PYRIMIDINAMINE
4,6-DIMETHYL-N-PHENYL-PYRIMIDIN-2-AMINE
MYTHOS
N-(4,6-DIMETHYL-2-PYRIMIDINYL)-N-PHENYLAMINE
N-PHENYL-4,6-DIMETHYL-2-PYRIMIDINAMINE
PYRIMETHANIL
SCALA
2-anilin-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine
n-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)aniline
Mytho
PYRIMETHANIL PESTANAL, 250 MG
2-Pyrimidinamine, 4,6-dimethyl-N-phenyl-
4,6-DIMETHYL-N-PHENYL-2-PYRIMIDINAMINE(PYRIMETHANIL)
Dynmethanil | [EINECS(EC#)]
414-220-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C12H13N3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00172113 | [Molecular Weight]
199.25 | [MOL File]
53112-28-0.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Pyrimethanil is a white to light yellow crystal-
line powder. Commercial product is available as a brown
emulsifiable concentrate. | [Melting point ]
96°C | [Boiling point ]
362.8±45.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.15 | [vapor pressure ]
2.2 x l0-5 Pa (25 °C) | [storage temp. ]
0-6°C | [solubility ]
DMSO: 130 mg/mL (652.45 mM) | [form ]
neat | [pka]
3.52 | [color ]
White to off-white | [Water Solubility ]
0.121 g/L (25 ºC) | [BRN ]
151589 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C12H13N3/c1-9-8-10(2)14-12(13-9)15-11-6-4-3-5-7-11/h3-8H,1-2H3,(H,13,14,15) | [InChIKey]
ZLIBICFPKPWGIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C1(NC2=CC=CC=C2)=NC(C)=CC(C)=N1 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
53112-28-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
53112-28-0(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
N | [Risk Statements ]
R51/53:Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment . | [Safety Statements ]
S60:This material and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste . | [RIDADR ]
UN 3077 | [WGK Germany ]
2 | [HS Code ]
2933599590 | [Hazardous Substances Data]
53112-28-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 (mg/kg): 4061-5358 orally in mice; 4150-5971 orally in rats; >5000 dermally in rats; LC50 (96 hr) in mirror carp, rainbow trout (mg/l): 35.36, 10.56 (Neumann) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Potential Exposure]
A pyrimidine fungicide used on
grapes, strawberries, tomatoes, onions, beans, cucumbers,
eggplant, and ornamental plants. | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any
contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek
medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the
skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately
with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.
If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,
begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions) if
breathing has stopped, and CPR if heart action has stopped.
Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical
has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large
quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an
unconscious person vomit. | [Shipping]
UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances,
liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous
hazardous material, Technical Name Required. UN3077
Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard
class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material,
Technical Name Required. | [Incompatibilities]
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates,
nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine,
bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo-
sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases,
strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. | [Chemical Properties]
Off-White Solid | [Chemical Properties]
Pyrimethanil is a white to light yellow crystal-
line powder. Commercial product is available as a brown
emulsifiable concentrate. | [Waste Disposal]
Containers must be disposed
of properly by following package label directions or by
contacting your local or federal environmental control
agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. If this
material cannot be disposed of according to label instruc-
tions, it may be dissolved or mixed with a combustible sol-
vent and burned in a chemical incinerator equipped with an
afterburner and scrubber. In accordance with 40CFR165,
follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and
pesticide containers. | [Uses]
Fungicide. | [Uses]
Pyrimethanil is a broad spectrum anilino-pyrimidine foliar fungicide. Pyrimethanil functions by inhibiting the biosynthesis of methionine in Botrytis cinerea. | [Uses]
Pyrimethanil provides both protective and curative control of
fungal diseases in pome fruits (leaf scab caused by Venturiu inaequalis),
vines, fruits, vegetables and ornamentals (grey mould) | [Definition]
ChEBI: A member of the class of aminopyrimidines that is N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine carrying two additional methyl substituents at positions 4 and 6. A fungicide used to control grey mould on fruit, vegetables and ornamentals as well as leaf sc
b on pome fruit. Also commonly employed to control Botrytis cinerea throughout the winemaking process in grapes, must, fermenting must and wine. | [Preparation]
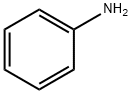
Pyrimethanil is produced by reaction of 2-bromo-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine with aniline. | [Synthesis Reference(s)]
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 30, p. 1942, 1982 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.30.1942 | [General Description]
Pyrimethanil is an anilino-pyrimidine, broad spectrum fungicide primarily used for the control of gray mould and leaf scab on fruits, vegetables and ornamentals. Its mode of action involves inhibition of the secretion of hydrolytic enzymes by the fungi during the infection process, thus stopping the further development of the disease. | [Agricultural Uses]
Fungicide: Used on grapes, strawberries, tomatoes, onions, beans, cucumbers, eggplant, and ornamental. | [Trade name]
SCALA®; SN 100309® | [Synthesis]
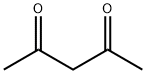
First, aniline and 50% aqueous cyanamide were added sequentially in an inert atmosphere reactor protected by nitrogen. Subsequently, 32% hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the reaction system to 2.5, after which the reaction mixture was gradually heated up from 45°C to 95°C within 2 hours, and the pH was maintained at 2.5 by adding hydrochloric acid during the heating process. 80°C was reached, acetylacetone was added dropwise to the reaction system, and at the same time, 50% sodium hydroxide solution was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the reaction system to 7.9, and the reaction was stirred and stirred for 1 hour to keep the temperature at this level. The reaction was maintained at this temperature and stirred for 1 h. At the end of the reaction, the reaction was allowed to stand and stratified, and the lower aqueous phase was separated and discarded. The upper organic phase was distilled at 750-35 mbar under reduced pressure, controlling the temperature at the bottom of the tower not to exceed 125°C, and recovering the excess acetylacetone for subsequent use. At the end of the distillation, the residue was cooled to 80 °C and diluted with the addition of isopropanol. The mixture was then slowly cooled to 0°C to precipitate a solid product, which was collected by filtration through a glass sand core funnel. The reactor was washed with a small amount of water and the washings were combined into the filtrate. The product was washed twice with isopropanol and placed in a vacuum drying oven and dried at 70 °C and 10 mbar. Finally, 324 g (1.626 mol) of 4,6-dimethyl-N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine was obtained in 81.3% yield of the theoretical value, with 97.6% purity by HPLC (internal standard method) or 99.9% purity by GC (area normalization method).
GC analysis conditions: 30 m DB-1701 capillary column (0.32 mm I.D., 0.25 μm film thickness), inlet temperature of 250 ℃, detector (FID) temperature of 300 ℃, injection volume of 0.2 μl (0.1 g/l methanol solution), programmed heating: 50 ℃ was held for 2 min, and then increased to 250 ℃ at 10 ℃/min for 8 min.
HPLC analysis conditions: Agilent 1100 series high performance liquid chromatograph; Nucleosil 120-5 C18 column (250×4 mm); injection volume 5 μl, flow rate 1 ml/min, room temperature detection, column pressure 90 bar, detection wavelength 268 nm, running time 8 min; mobile phase: 250 mL Millipore water+ 750 mL acetonitrile+ 1 g of methanol solution. 750 mL acetonitrile + 1 g ammonium acetate; sample solvent: 250 mL Millipore water + 750 mL acetonitrile; quantitative analysis was carried out using pyrimethamine standards of known concentration. | [Metabolic pathway]
Limited data are available in the open literature. Information presented in
this summary is abstracted from the data evaluation published by the
Pesticide Safety Directorate (PSD, 1995). Hydroxylation at the methyl,
phenyl or pyrimidine moiety is the primary metabolic pathway of pyrimethanil
in soil, plants and animals. Cleavage of the aniho-pyrimidine
linkage was observed as a minor metabolic reaction. The formation of
nitro- analogues of pyrimethanil is a novel nitration reaction observed in
the soil metabolism study (Scheme 1). | [Degradation]
Pyrimethanil (1) is stable to hydrolytic degradation in the environmentally
relevant pH range (5-9) at 22-50 °C.
Pyrimethanil degraded rapidly at pH 4 and 30 °C (DT50 1 day) when the
sterile buffered solution was exposed to mercury arc lamp (200-500 nm).
The DT50 of pyrimethanil in pH 7 solution under the same photolysis test
conditions was ca.77 days. There is no information on the chemical nature
of pyrimethanil aqueous photolysis products. | [References]
[1] Patent: US2011/137033, 2011, A1. Location in patent: Page/Page column 2 |
|
|