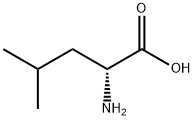
| Identification | More | [Name]
N-Acetyl-D-leucine | [CAS]
19764-30-8 | [Synonyms]
AC-D-LEUCINE
AC-D-LEU-OH
ACETYL-D-LEUCINE
N-ACETYL-D-LEUCINE
N-ALPHA-ACETYL-D-LEUCINE
n-acetyl-d-leucinesigmagr
N-Acetyle-D-Leucine
Ace-D-Leu-OH
N-ACETYL-L-LEUCINE:AC-D-LEU-OH
2-(Acetylamino)-4-methylpentanoic acid
N-ACETHY-D-LEUCINE
N-Ac-D-Leucine
2-Acetylamino-4-methylvaleric acid
N-Acetyl-2-isobutylglycine
D-2-Acetylamino-4-methylvaleric acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
1533716-785-6 | [Molecular Formula]
C8H15NO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00066069 | [Molecular Weight]
173.21 | [MOL File]
19764-30-8.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
176-177C | [Boiling point ]
369.7±25.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.069±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [refractive index ]
23 ° (C=4, EtOH) | [storage temp. ]
−20°C
| [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Ethanol (Slightly, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
3.67±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White to Off-White | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C8H15NO3/c1-5(2)4-7(8(11)12)9-6(3)10/h5,7H,4H2,1-3H3,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/t7-/m1/s1 | [InChIKey]
WXNXCEHXYPACJF-SSDOTTSWSA-N | [SMILES]
C(O)(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC(C)=O | [CAS DataBase Reference]
19764-30-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [HS Code ]
29241990 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White to off-white powder | [Uses]
N-Acetyl-D-leucine may be used with other D-aminoacylated amino acids as a substrate for the identification, differentiation and characterization of D-aminoacylase(s)/amidohydrolase(s). | [Definition]
ChEBI: N-acetyl-D-leucine is the N-acetyl derivative of D-leucine. It is a N-acetyl-D-amino acid and a D-leucine derivative. It is a conjugate acid of a N-acetyl-D-leucinate. It is an enantiomer of a N-acetyl-L-leucine. | [Biological Activity]
N-Acetyl-D-leucine is a substrate for D-aminoacylase from Alcaligenes xylosoxydans subsp. xylosoxydans A-6. N-Acetyl-D-leucine is used to help differentiate members of the amidohydrolase enzyme superfamily. It is a preferred substrate of Gox1177 from Gluconobacter oxidans. | [Synthesis]
Procedure: the preparation of compound 10 (N-acetyl-D-leucine) was carried out by an improved prior art method (see Am. Chem. Soc., 1951, 73, 3359-3360) as follows:
In a 22-liter four-neck flask equipped with a thermocouple controller, an overhead mechanical stirrer, and two 2.0-liter dosing funnels. Deionized water (2.45 L) and D-leucine (99% e.e., 917.0 g, 7.0 mol) were added to the flask and stirring was initiated. Acetic anhydride (99%, 2142.0 g, 21.0 mol) and 20% aqueous NaOH solution (2.45 L, 49.0 mol) were added simultaneously and slowly dropwise over a period of 3 to 4 h. The temperature of the reaction was maintained between 5 and 15°C. The reaction temperature was controlled by adjusting the titration rate of the basic solution and acetic anhydride as well as wet ice cooling. The pH of the reaction mixture was maintained in the slightly basic range (pH 8-9) during the reaction using pH test paper every 10-15 min. The reaction process was monitored by HPLC and LC-MS.
After completion of addition, stirring of the reaction mixture was continued for 1 h. Subsequently, acidification was carried out by slow addition of 37% HCl solution (4.76 L, 49.0 mol) over a period of 30 min. After acidification, a white solid precipitated and the slurry was stirred at 5°C to 15°C for 2 hours. The solid product was separated by filtration, washed with deionized water (2.0 L x 7), dried by air suction for 3 h, and finally dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 16 h (until the weight of the solid no longer decreased).
Finally 1083 g (89% yield) of N-acetyl-D-leucine (compound 10) was obtained as a white powdery solid with high optical purity (>97% e.e.). The structure of the product was confirmed by 1H-NMR and LC-MS analyses and it could be used in subsequent steps without further purification. | [in vivo]
N-Acetyl-R-leucine (24 mg per rat; i.v.; once a day) has no significant effect on the compensation of nystagmus and postural imbalance scores in rats[4].
| [References]
[1] Patent: WO2006/93719, 2006, A1. Location in patent: Page/Page column 34; 35
[2] Organic Process Research and Development, 2005, vol. 9, # 5, p. 640 - 645 |
|
|