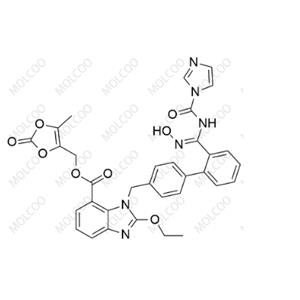
Azilsartan Impurity 141 NEW
| Price | Get Latest Price | ||
| Package | 10mg | 50mg | 100mg |
| Min. Order: | 10mg |
| Supply Ability: | 1000 |
| Update Time: | 2025-07-18 |
Product Details
| Product Name: Azilsartan Impurity 141 | CAS No.: 1514933-19-7 |
| Min. Order: 10mg | Purity: 99%+ HPLC |
| Supply Ability: 1000 | Release date: 2025/07/18 |
| Molecular formula: C33H28N6O8 |
Diphenhydramine N-Oxide

WhatsAPP: +86 17386083646
E-mail: anna@molcoo.com.
Product Information
Product Number: A006141
English Name: Azilsartan Impurity 141
English Alias: (Z)-(5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-((2'-(N'-hydroxy-N-(1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)carbamimidoyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-7-carboxylate
CAS Number: 1514933-19-7
Molecular Formula: C??H??N?O?
Molecular Weight: 636.61
Advantages
Well-defined and distinct structure: Contains benzimidazole, biphenyl, imidazole carbonyl carbamimidoyl, and dioxol-4-ylmethyl ester groups, differing from azilsartan mainly in (Z)-configuration and retained ester group. The synergistic effect of polyheterocycles and multiple functional groups (hydroxyl, carbonyl, ester) endows unique polarity and retention behavior, enabling accurate identification via HPLC and LC-MS as a specific marker for impurity detection;
High stability and traceability: The conjugated system formed by multiple amide bonds, ester groups, and heterocycles is highly stable under neutral conditions. As a by-product of incomplete acylation or cyclization in azilsartan synthesis, it directly reflects the efficiency of key steps, improving the accuracy of process tracing;
High detection sensitivity: The polycyclic conjugated system has strong UV absorption (250-270nm), combined with the characteristic molecular ion peak in mass spectrometry (m/z 637 [M+H]?), enabling trace analysis (ppb level) via LC-MS, compatible with the impurity detection system of angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonists.
Applications
Pharmaceutical quality control: Used as an impurity reference standard to identify and quantify Azilsartan Impurity 141 in azilsartan APIs and formulations, ensuring that impurities generated during synthesis meet quality standards;
Synthesis process optimization: By monitoring the content of this impurity, optimize parameters such as acylation reagent ratio and cyclization temperature to improve the selectivity of the target product and reduce the generation of by-products;
Impurity profile enrichment: Used to supplement the impurity profile of azilsartan, providing key data for a comprehensive evaluation of drug purity and potential safety risks, supporting drug registration applications.
Background Description
Research Status
Optimization of detection methods: Developing ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) methods to achieve simultaneous quantification of this impurity and azilsartan in complex matrices by utilizing the difference in fragment ions (such as characteristic fragments of dioxolane esters), with a detection limit as low as 0.1 ppb;
Study on configuration conversion: By simulating different temperatures and solvent conditions, study the conversion kinetics between Z-isomer and target configuration, and clarify the influence of reaction conditions on configuration selectivity;
Improvement of synthesis process: Using chiral catalysts to regulate the stereoselectivity of cyclization reactions, reducing the generation rate of Z-type impurities. Relevant studies have controlled the content of this impurity below 0.05%;
Stability evaluation: Investigate the degradation behavior of this impurity under different pH and light conditions to provide reference for the design of storage conditions for azilsartan preparations.
Product Information
Product Number: A006141
English Name: Azilsartan Impurity 141
English Alias: (Z)-(5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-1-((2'-(N'-hydroxy-N-(1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)carbamimidoyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-7-carboxylate
CAS Number: 1514933-19-7
Molecular Formula: C??H??N?O?
Molecular Weight: 636.61
Advantages
Well-defined and distinct structure: Contains benzimidazole, biphenyl, imidazole carbonyl carbamimidoyl, and dioxol-4-ylmethyl ester groups, differing from azilsartan mainly in (Z)-configuration and retained ester group. The synergistic effect of polyheterocycles and multiple functional groups (hydroxyl, carbonyl, ester) endows unique polarity and retention behavior, enabling accurate identification via HPLC and LC-MS as a specific marker for impurity detection;
High stability and traceability: The conjugated system formed by multiple amide bonds, ester groups, and heterocycles is highly stable under neutral conditions. As a by-product of incomplete acylation or cyclization in azilsartan synthesis, it directly reflects the efficiency of key steps, improving the accuracy of process tracing;
High detection sensitivity: The polycyclic conjugated system has strong UV absorption (250-270nm), combined with the characteristic molecular ion peak in mass spectrometry (m/z 637 [M+H]?), enabling trace analysis (ppb level) via LC-MS, compatible with the impurity detection system of angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonists.
Applications
Pharmaceutical quality control: Used as an impurity reference standard to identify and quantify Azilsartan Impurity 141 in azilsartan APIs and formulations, ensuring that impurities generated during synthesis meet quality standards;
Synthesis process optimization: By monitoring the content of this impurity, optimize parameters such as acylation reagent ratio and cyclization temperature to improve the selectivity of the target product and reduce the generation of by-products;
Impurity profile enrichment: Used to supplement the impurity profile of azilsartan, providing key data for a comprehensive evaluation of drug purity and potential safety risks, supporting drug registration applications.
Background Description
Research Status
Optimization of detection methods: Developing ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) methods to achieve simultaneous quantification of this impurity and azilsartan in complex matrices by utilizing the difference in fragment ions (such as characteristic fragments of dioxolane esters), with a detection limit as low as 0.1 ppb;
Study on configuration conversion: By simulating different temperatures and solvent conditions, study the conversion kinetics between Z-isomer and target configuration, and clarify the influence of reaction conditions on configuration selectivity;
Improvement of synthesis process: Using chiral catalysts to regulate the stereoselectivity of cyclization reactions, reducing the generation rate of Z-type impurities. Relevant studies have controlled the content of this impurity below 0.05%;
Stability evaluation: Investigate the degradation behavior of this impurity under different pH and light conditions to provide reference for the design of storage conditions for azilsartan preparations.
This product is intended for laboratory use only!
WhatsAPP: +86 17386083646
E-mail: anna@molcoo.com
Company Profile Introduction
You may like
Recommended supplier
| Product name | Price | Suppliers | Update time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $0.00/5mg |
VIP1Y
|
Guangzhou Tosun Pharmaceutical Ltd
|
2025-01-23 | |
| $0.00/25KG |
VIP6Y
|
Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd
|
2024-10-22 | |
| $0.00/10mg |
VIP2Y
|
ShenZhen H&D Pharmaceutical Technology Co., LTD
|
2024-06-04 |









 China
China