
5-Chloroindole NEW
| Price | Get Latest Price | |
| Package | 1kg | 25kg |
| Min. Order: | 1kg |
| Supply Ability: | 1000kg |
| Update Time: | 2025-08-15 |
Product Details
| Product Name: 5-Chloroindole | CAS No.: 17422-32-1 |
| EC-No.: 241-448-9 | Min. Order: 1kg |
| Purity: 98% | Supply Ability: 1000kg |
| Release date: 2025/08/15 |
5-Chloroindole: A Comprehensive Overview
Chemical Structure:
5-Chloroindole is a halogenated derivative of indole, a bicyclic aromatic compound composed of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring (containing one nitrogen atom). The chlorine atom is attached to the 5-position of the benzene ring. Its molecular formula is C8H6ClN.
Synthesis:
Direct Chlorination: Indole can undergo electrophilic substitution with chlorinating agents like or chlorine gas. However, regioselectivity is challenging due to indole’s inherent reactivity (typically favoring substitution at the 3-position).
Directed Synthesis: To target the 5-position, methods like the Fischer indole synthesis or cross-coupling reactions may use pre-functionalized precursors (e.g., chlorinated phenylhydrazines or intermediates).
Sandmeyer Reaction: Chlorination via diazonium intermediates can also be employed for regioselective substitution.
Physical and Chemical Properties:
Appearance: Typically a white to off-white crystalline solid.
Melting Point: ~90–95°C (varies with purity).
Solubility: Soluble in organic solvents (e.g., dichloromethane, ethanol), sparingly soluble in water.
Reactivity:
The chlorine atom is meta-directing and electron-withdrawing, influencing further electrophilic substitution (e.g., sulfonation, nitration).
The nitrogen in the pyrrole ring contributes to π-electron richness, enabling reactions at the 2- and 3-positions.
Applications:
Pharmaceuticals: Key intermediate in synthesizing bioactive compounds, including serotonin receptor modulators and kinase inhibitors.
Agrochemicals: Used in the design of herbicides and fungicides.
Material Science: Building block for organic semiconductors or fluorescent dyes.
Research: Probe for studying enzyme inhibition or ligand-receptor interactions.
Safety and Handling:
Toxicity: May cause skin/eye irritation and respiratory discomfort.
Precautions: Use gloves, goggles, and work in a fume hood. Consult SDS for specific guidelines.
Natural Occurrence:
Rare in nature; primarily synthetic. Chlorinated indoles may arise in trace amounts via environmental halogenation processes.
Isomerism:
Structural isomers include 4-chloroindole, 6-chloroindole, and 7-chloroindole, differing in chlorine placement and properties.
Comparison to 2-Furoic Acid:
Unlike 2-furoic acid (a furan-based carboxylic acid), 5-chloroindole features a nitrogen-containing aromatic system with a halogen substituent. Both serve as versatile intermediates but in distinct contexts (e.g., indoles in alkaloid-inspired drugs vs. furoic acids in polymer chemistry).
5-Chloroindole’s unique electronic and structural features make it valuable in medicinal chemistry and organic synthesis, particularly where halogenated heterocycles are required.
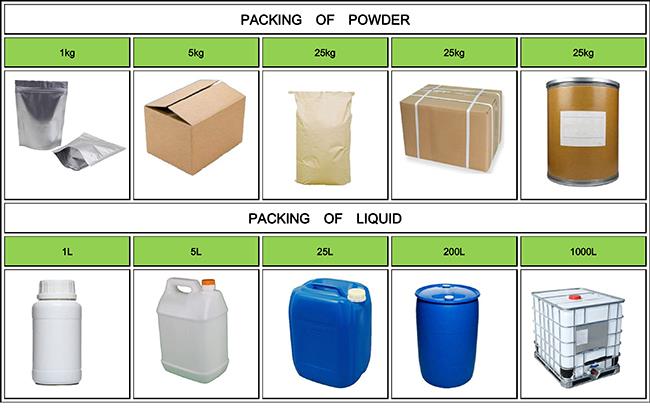


Company Profile Introduction
You may like
Recommended supplier
| Product name | Price | Suppliers | Update time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $0.00/25KG |
VIP3Y
|
Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd
|
2024-10-29 | |
| $0.00/1kg |
VIP3Y
|
Henan Aochuang Chemical Co.,Ltd.
|
2022-09-26 | |
| $1.00/1KG |
Chemwill Asia Co.,Ltd.
|
2019-04-03 | ||
| $8.00/1kg |
VIP8Y
|
Career Henan Chemical Co
|
2018-12-17 |
- Since: 2006-04-03
- Address: Room 2015, No.2 Building Kaixin Mansion, No.107 Jinqiao Ave, Wuhan, China
+86-13986145403
info@fortunachem.com











 China
China