| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Tat-NR2B9c | [CAS]
500992-11-0 | [Synonyms]
Tat-NR2B9c
Tat-NR2B9c/NA-1
Tat-NR2B9c, >98%
500992-11-0/1834571-04-8
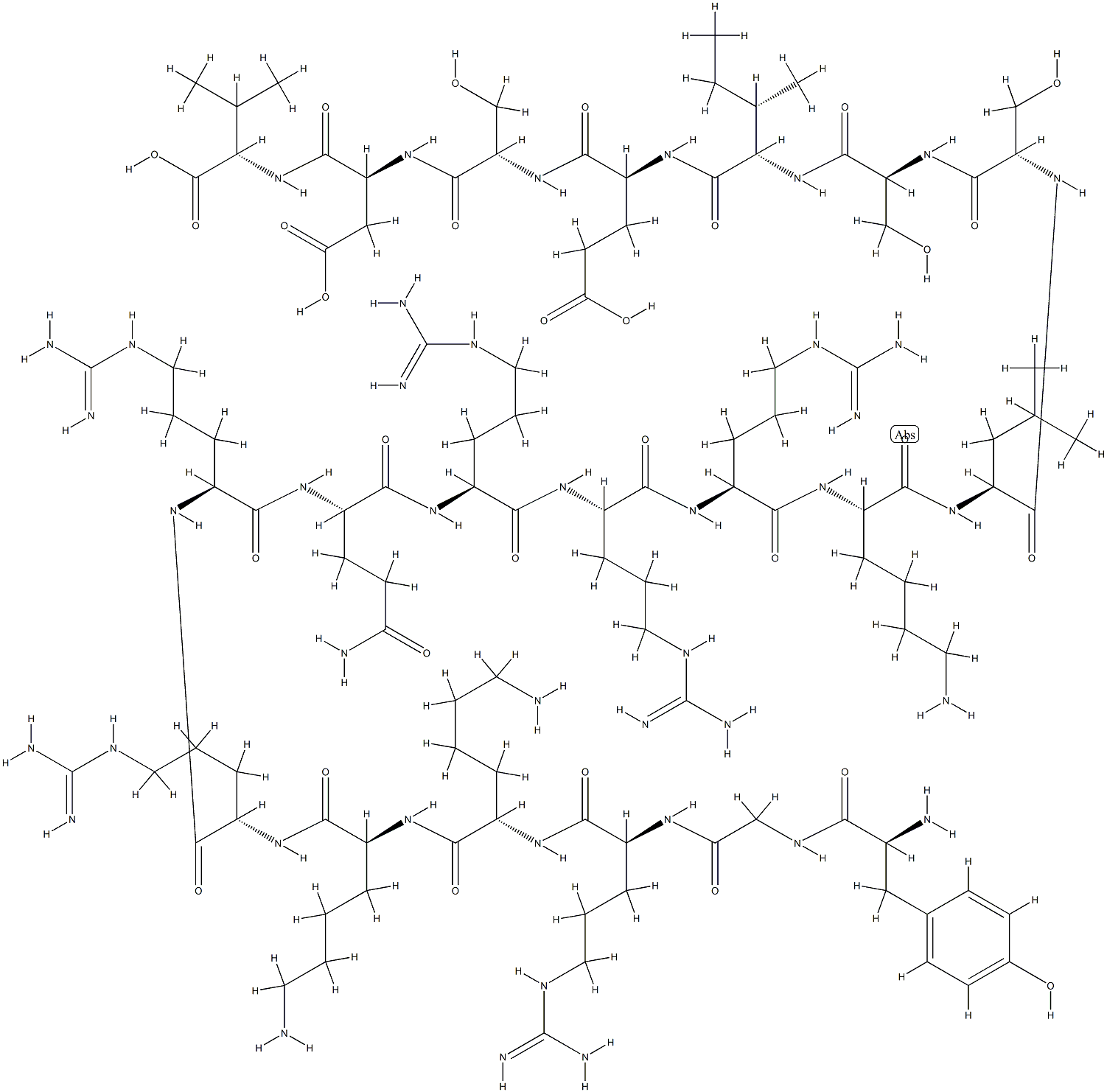
L-Valine, L-tyrosylglycyl-L-arginyl-L-lysyl-L-lysyl-L-arginyl-L-arginyl-L-glutaminyl-L-arginyl-L-arginyl-L-arginyl-L-lysyl-L-leucyl-L-seryl-L-seryl-L-isoleucyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-seryl-L-α-aspartyl- | [Molecular Formula]
C105H188N42O30 | [MOL File]
500992-11-0.mol | [Molecular Weight]
2518.88 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [density ]
1.52±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
White to off-white | [Water Solubility ]
Water : ≥ 50 mg/mL (19.85 mM) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Tat-NR2B9c (Tat-NR2Bct; NA-1) is a postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) inhibitor, with EC50 values of 6.7 nM and 670 nM for PSD-95d2 (PSD-95 PDZ domain 2) and PSD-95d1, respectively. Tat-NR2B9c disrupts the PSD-95/NMDAR interaction, inhibiting NR2A and NR2B binding to PSD-95 with IC50 values of 0.5 μM and 8 μM, respectively. Tat-NR2B9c also inhibits?neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS)/PSD-95?interaction, and possesses neuroprotective efficacy[1][2][5]. | [Biological Activity]
Tat-NR2B9c (NA-1) is a 20-mer peptide composed of a membrane-permeant HIV-1 T at protein transduction domain sequence (a.a. 47-57) N-terminal to the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) GluN2B carboxyl tail sequence KLSSIESDV th at blocks intracellular NMDAR-PSD-95 interaction-induced neurotoxic signaling without affecting NMDAR-mediated synaptic activity or calcium influx. NA-1 protects cultured cortical neurons from NMDA excitotoxicity (50 nM; 20/40/100 μM NMDA) and reduces focal ischemic brain damage in rats in vivo (3 μmol/kg iv. bolus 1 hr post MCAO onset). | [in vivo]
Tat-NR2B9c (10?nmol/g, i.v.) reduces infarction volume of male C57BL/6 mice, but has no effect at 3?nM/g[3]. | [IC 50]
NMDA Receptor; nNOS | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [References]
[1] Cui H, et al. PDZ protein interactions underlying NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity and neuroprotection by PSD-95 inhibitors. J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 12;27(37):9901-15. DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1464-07.2007
[2] Fan J, et al. P38 MAPK is involved in enhanced NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity in YAC transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Mar;45(3):999-1009. DOI:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.019
[3] Teves LM, et al. Efficacy of the PSD95 inhibitor Tat-NR2B9c in mice requires dose translation between species. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 Mar;36(3):555-61. DOI:10.1177/0271678X15612099
[4] Jing Fan, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Subunit- And Neuronal-Type Dependence of Excitotoxic Signaling Through Post-Synaptic Density 9. J Neurochem. 2010 Nov;115(4):1045-56. DOI:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06994.x |
|
| Company Name: |
Musechem
|
| Tel: |
+1-800-259-7612 |
| Website: |
www.musechem.com |
|