| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
[(Difluoromethyl)sulfonyl]benzene | [CAS]
1535-65-5 | [Synonyms]
PhSO2CF2H
Phenyl difluoromethyl sulfone
Difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone
Difluoromethylphenylsulfone,95%
[(Difluoromethyl)sulfonyl]benzene
Difluoromethyl Phenyl Sulfone >
1-(difluoroMethylsulfonyl)benzene
Difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone >=97%
Benzene, [(difluoroMethyl)sulfonyl]- | [Molecular Formula]
C7H6F2O2S | [MDL Number]
MFCD01050170 | [MOL File]
1535-65-5.mol | [Molecular Weight]
192.18 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
24-25℃ | [Boiling point ]
115-120 °C(Press: 7 Torr) | [density ]
1.348 | [Fp ]
128℃ | [refractive index ]
1.5000 | [storage temp. ]
Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,2-8°C | [solubility ]
Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
liquid | [color ]
colorless | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in chloroform and water. | [BRN ]
2259218 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C7H6F2O2S/c8-7(9)12(10,11)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5,7H | [InChIKey]
LRHDNAVPELLXDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
C1(S(C(F)F)(=O)=O)=CC=CC=C1 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone is a powerful nucleophilic difluoromethylation reagent due to the
high reactivity of the sulfonyl-stabilized difluoromethyl anion towards many electrophiles
including carbonyls, imines, alkyl halides, and cyclic sulfates and sulfamidates. In the nucleophilic
reaction step, depending on the substrate structure, strong bases are used to generate the
nucleophilic (phenylsulfonyl)difluoromethyl anion in situ. In the desulfonylation step,
sodium/mercury amalgam and magnesium are the commonly used reductive reagents. Besides, the
(phenylsulfonyl)difluoromethylated compounds can undergo β-elimination to afford
gem-difluoroalkenes. | [Chemical Properties]
light yellow liquid | [Uses]
Efficient reagent for difluoromethylation of carbonyls and aldehydes. | [Reactions]
(1) Difluoromethylation of alkyl halides.

(2) Difluoromethylation of aldehydes and ketones.

(3) Difluoromethylenation of aldimines and ketimines.

(4) Difluoromethylation of cyclic sulfates and sulfamidates.

(5) (Phenylsulfonyl)difluoromethylation of carboxylic acid esters.

(6) Difluoromethylenation of alkyl halides.
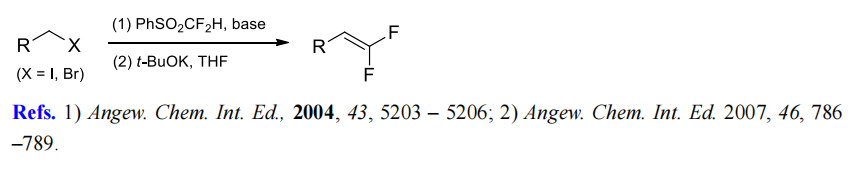
(7) Difluoromethylenation of aromatic aldehydes.
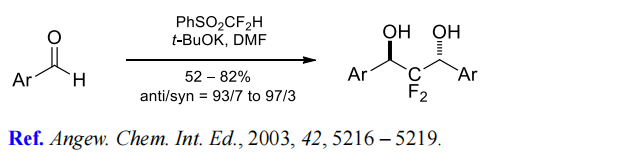
| [Synthesis]
To an anhydrous dichloromethane (69 mL) solution of difluoromethyl phenyl sulfide (3.98 g, 25 mmol) was added solid m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (m-CPBA, 15.9 g, 92.0 mmol) in batches at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was gradually warmed to room temperature and stirred overnight. Upon completion of the reaction, dichloromethane (50 mL) was added to dilute the mixture, and the mixture was washed sequentially with 10% aqueous sodium sulfite (2 × 100 mL), 5% aqueous sodium bicarbonate (4 × 50 mL) and saturated saline (2 × 100 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography with dichloromethane and hexane (3:1, v/v) as eluents. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) showed an Rf value of 0.40 (dichloromethane/hexane, 3:1). 4.24 g of difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone was finally obtained in 88% (22.1 mmol) yield. The structure of the product was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen (1H NMR, 300 MHz, CDCl3), carbon (13C NMR, 101 MHz, CDCl3) and fluorine (19F NMR, 282 MHz, CDCl3) spectra, and the data were in agreement with the literature reports. | [References]
[1] G. PRAKASH. Nucleophilic difluoromethylation of primary alkyl halides using difluoromethyl phenyl sulfone as a difluoromethyl anion equivalent.[J]. Organic Letters, 2004. DOI:10.1002/CHIN.200509059.
[2] G. K. SURYA PRAKASH. Difluoromethyl Phenyl Sulfone, a Difluoromethylidene Equivalent: Use in the Synthesis of 1,1-Difluoro-1-alkenes.[J]. ChemInform, 2005. DOI:10.1002/chin.200504098.
[3] G. K. SURYA PRAKASH. Nucleophilic Difluoromethylation of Primary Alkyl Halides Using Difluoromethyl Phenyl Sulfone as a Difluoromethyl Anion Equivalent[J]. Organic Letters, 2004, 6 23: 4315-4317. DOI:10.1021/ol048166i.
|
|
|