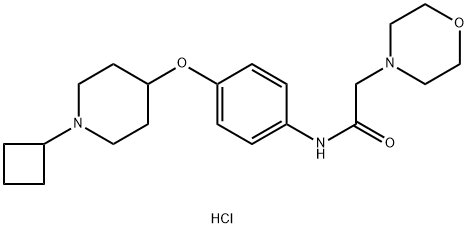
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
SUVN-G3031 hydrochloride | [CAS]
1394808-20-8 | [Synonyms]
SUVN-G3031 HCl
SUVN-G3031 hydrochloride
SUVN-G3031 dihydrochloride | [Molecular Formula]
C21H32ClN3O3 | [MOL File]
1394808-20-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
409.96 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
DMSO : 62.5 mg/mL (140.01 mM; ultrasonic and warming and heat to 60°C) | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
Off-white to light yellow |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Samelisant (SUVN-G3031) is a potent and selective histamine H3 receptor (H3R) inverse agonist with good brain penetration and oral bioavailability. Samelisant has a similar binding affinity towards human (hH3R; Ki=8.7 nM) and rat (rH3R;Ki=9.8 nM) H3R indicating no inter-species differences. Samelisant can be used for the research of sleep-related disorders[1]. | [in vivo]
Treatment with Samelisant (10 and 30 mg/kg, p.o.) produces a significant increase in wakefulness with a concomitant decrease in non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM) sleep in orexin knockout mice subjected to sleep electroencephalography (EEG)[1].
Samelisant also produces a significant decrease in direct rapid eye movement (REM) sleep onset (DREM) episodes, demonstrating its anticataplectic effects in an animal model relevant to narcolepsy[1].
Samelisant treatment in mice produces a dose-dependent increase in tele-methylhistamine levels indicating the activation of histaminergic neurotransmission[1]. | Animal Model: | Male Wistar rats or male C57BL6J mice[1] | | Dosage: | 1, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg | | Administration: | Oral administration | | Result: | Produced a dose-dependent increase in t-MH levels in the frontal cortex, hypothalamus and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of male Wistar rats.
Produced a significant increase in t-MH levels of the frontal cortex, striatum and hypothalamus in mice.
|
| [References]
[1] Ramakrishna Nirogi, et al. Samelisant (SUVN-G3031), a potent, selective and orally active histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist for the potential treatment of narcolepsy: pharmacological and neurochemical characterisation. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 DOI:10.1007/s00213-021-05779-x |
|
|